The downfall of most software projects isn’t in the testing phase, it’s in the misalignments and assumptions made at the very start.
When teams don’t ask the right questions early on, they often end up building something users didn’t want. The problem? Skipping or rushing the requirements elicitation process.
According to PMI’s Pulse of the Profession report, 39% of project failures are caused by poor requirements elicitation and management.
This step isn’t about writing specs. It’s about listening, observing, and asking why. A missed requirement now can turn into months of rework later.
Let’s understand what requirements elicitation is, its importance for product teams, best practices and techniques for effective requirements elicitation, and how to use AI for the same.
What is Requirements Elicitation?
Requirements Elicitation is a process in software engineering where product team members interact with stakeholders to understand what they expect from the software being developed.
It’s more conversation than documentation. You ask, they explain. Sometimes you get straight answers. Sometimes you have to dig. And often, the real needs aren’t said out loud until you ask a few more questions.
You’re not jumping into solutions yet. You’re still trying to understand the problem clearly: what should the software do, who will use it, and what can’t it do?
Without this step, the risk of wrong assumptions increases, and that often leads to rework, delays, or features nobody asked for.
Key Steps in the Requirements Elicitation Process
Requirements elicitation is a step-by-step process that business analysts and product team members should follow to gather requirements that are suitable for the software product’s goals. Here, we have covered the 6-step requirements elicitation process:
1. Identify Stakeholders
The first step is to identify relevant stakeholders, who are people involved in the software project. Stakeholders could be:
- End-users
- Project sponsors
- Clients
- Regulatory authorities
- Support teams
Later, business analysts interact with these people to collect requirements and understand software goals.
2. Understand the Business Objectives and Goals
The next step is to understand the business goals and what the business is trying to achieve. It will help business analysts to prepare the correct questions to ask stakeholders.
3. Select the Appropriate Elicitation Technique
Next, select the appropriate elicitation technique to interact with stakeholders. Also, make sure that all stakeholders are comfortable with the selected technique. Common techniques include:
- Stakeholder interview
- Document analysis
- Prototyping
- Questionnaire
- Brainstorming sessions
We have covered these techniques in depth in the next section.
If you have selected multiple techniques, for each technique, prepare questions and tools that you are going to use. That will save your time in later stages.
4. Conduct the Elicitation Session
Once the elicitation method is selected, conduct the sessions with stakeholders. Make sure to take proper notes, ask follow-up questions, and even if you have a small doubt, don’t hesitate to ask.
5. Document Requirements
Next, business analysts evaluate the requirements and document them. It helps development teams and stakeholders to visualize the requirements.
6. Review Requirements
In the final stage, business analysts conduct a review session with stakeholders and other team members to review requirements. It is very important to ensure nothing is missed and all requirements are clear and align with the business goals.
Best Requirements Elicitation Techniques
There are multiple techniques available to elicit requirements, and we have covered a few of them that are commonly used:
1. Brainstorming Sessions
In brainstorming sessions, business analysts gather people from different backgrounds and take their input in a free-flow format. This method can be useful when you need to collect a wide range of ideas about business processes, goals, needs, and objectives quickly.
2. Interviews
Interviewing stakeholders is another important elicitation technique. It allows business analysts to talk with stakeholders in a one-on-one manner and ask open-ended questions.
You should choose this technique when you want to dig deep into a person’s specific needs, pain points, and expectations.
3. Surveys and Questionnaires
When you want to collect data from a large audience, such as product end-users, you can use a survey and questionnaire method.
In this method, you need to prepare a form with a set of questions, send it to a group of users, collect responses, and analyze them. It won’t provide you with in-depth insights like an interview, but it’s useful for identifying trends.
4. Document Analysis
A document analysis technique involves reviewing and analyzing the existing software documents, such as product manuals, policy documents, or system logs. By doing so, business analysts can identify missing requirements and decide what to add in the next iteration of the software development.
5. Focus Groups
You gather a small set of users who share similar roles or daily tasks. Instead of asking one person at a time, they talk as a group. People often build on each other’s thoughts, which brings out needs they may not mention alone. It’s also a good way to see what different users agree or disagree on.
6. Requirements Workshops
These are longer sessions where people from different departments sit together, including users, business owners, and maybe tech leads. Everyone looks at the same problem and works through it piece by piece. You don’t just collect input, but you settle disputes, clear up confusion, and decide what matters most.
7. Prototyping
Instead of waiting for full development, you create a basic mock-up that is just enough to show the layout or flow. Users can react to something visual, which often brings out feedback they wouldn’t share in a meeting. It helps clear confusion early and avoids building features based on guesses.
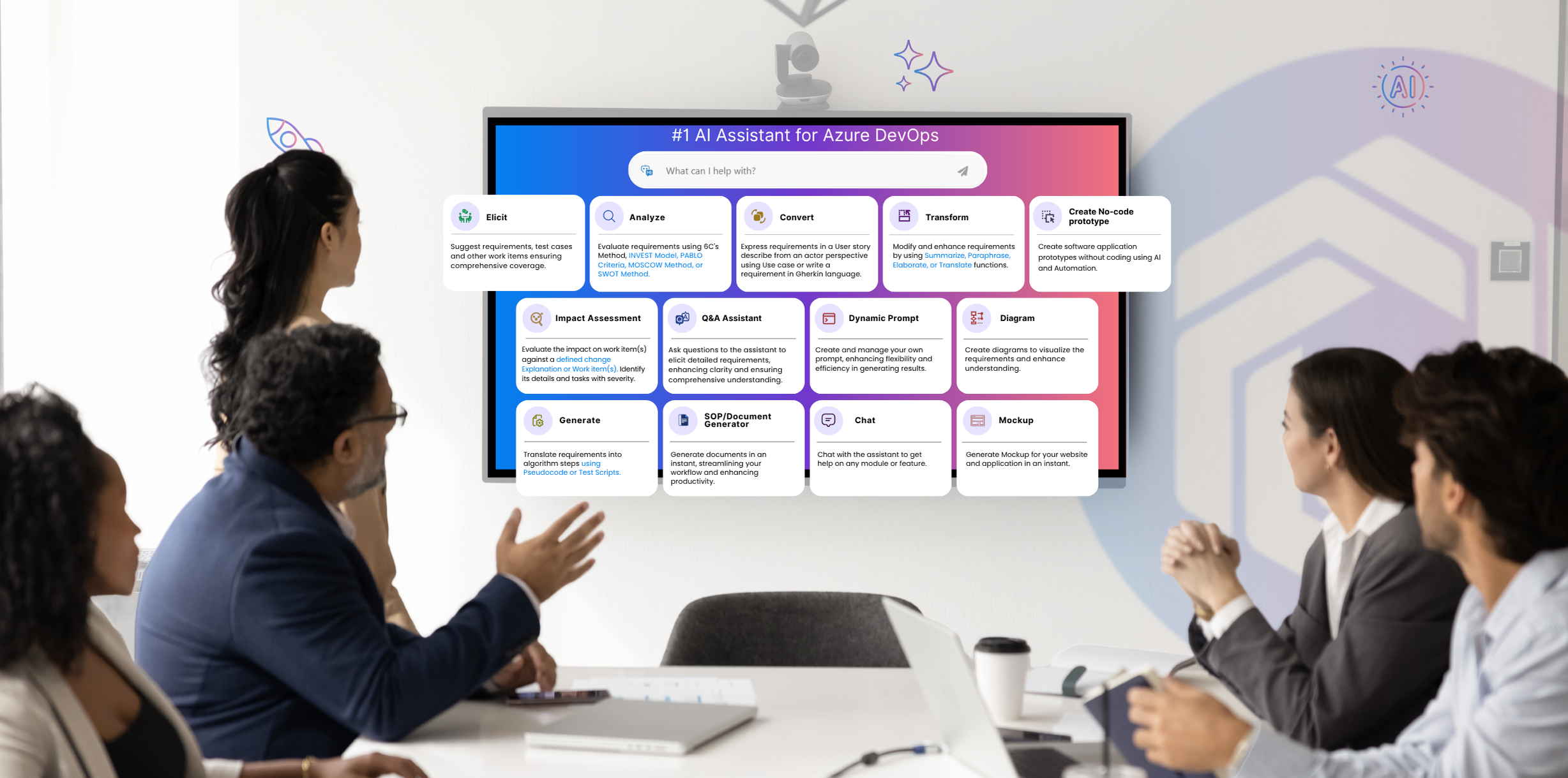
Using Copilot4DevOps to Automate Requirements Elicitation Using AI
Manual requirements gathering takes time. You talk to people, jot down notes, clean them up, and then rewrite everything in a proper format. It’s easy to miss things or forget details later.
However, AI requirements elicitation tools like Copilot4DevOps help cut down on that effort. It works as a built-in requirements management AI assistant within Azure DevOps.
To start using Copilot4DevOps:
- You need to pick up any work item within Azure DevOps and open up Copilot4DevOps from there.
- Select what kind of work items you want to generate, such as a user story, a test case, an epic, a feature, etc.
- And just click on the “Generate” button.
That’s all. Copilot4DevOps generates new work items with a title and description based on the referenced work item data.
Check the full video tutorial on how the elicit function of Copilot4DevOps works:
For teams dealing with tight timelines or scattered inputs, this can save hours every week. Whether you’re building banking apps, healthcare portals, or internal tools, it helps teams collect and format requirements without starting from scratch.
Try it Yourself
Ready to transform your DevOps with Copilot4DevOps?
Get a free trial today.